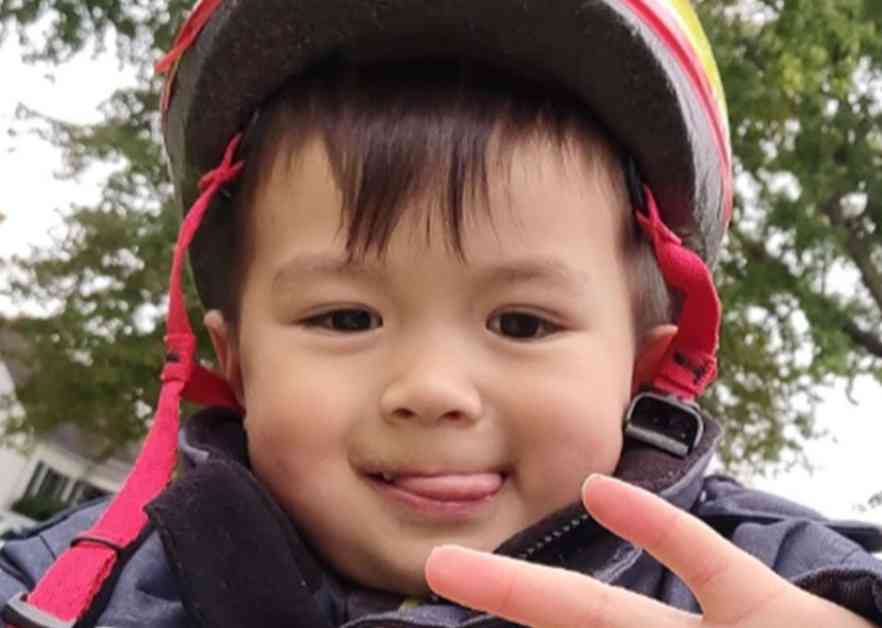
The heartbreaking incident involving the death of five-year-old Thomas Cooper inside a hyperbaric chamber at The Oxford Centre in Troy, Michigan, has sparked concerns about the safety of such treatments. The tragedy unfolded when the chamber exploded, resulting in Thomas losing his life as his mother, Annie Cooper, watched in horror on Friday, 31 January. Despite the swift arrival of emergency services, Thomas had already succumbed to his injuries by the time they reached the scene. Reports indicated that Annie, who was present with her son during the incident, suffered injuries to her arm while attempting to rescue him.
The Oxford Centre, a facility that has been offering hyperbaric oxygen therapy for over 15 years, expressed shock and disbelief at the unprecedented nature of the accident. The tragic event has prompted a closer examination of safety protocols at hyperbaric therapy centers, particularly those operating outside of regulated medical environments.
Understanding Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a treatment method that involves administering 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber to enhance the delivery of oxygen to the body’s tissues. While this therapy has traditionally been used to address various medical conditions like carbon monoxide poisoning, chronic wounds, and sports injuries, its application for conditions such as ADHD or autism lacks recognition from health authorities.
Despite the lack of approval for certain conditions, the Oxford Centre in Troy was offering hyperbaric oxygen therapy for unapproved uses, including providing treatment for Thomas Cooper, who was undergoing therapy for sleep apnea and ADHD. The Cooper family reportedly paid $8000 for 40 treatment sessions at the facility.
Examining Safety Concerns
The tragic incident involving Thomas Cooper has raised significant questions about the potential dangers associated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. While occurrences of chamber explosions are rare, experts note that the pressurized environment in hyperbaric chambers can lead to highly combustible situations when combined with pure oxygen. The Troy Fire Department confirmed that the explosion at the Oxford Centre was caused by the presence of oxygen in the chamber, which supports combustion.
James Harrington, the family’s attorney, emphasized the need for stricter regulation and oversight of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in light of the tragedy. He expressed concerns about the safety of these treatments and pledged to pursue legal action to ensure accountability and prevent similar incidents in the future.
Call for Enhanced Regulation
Experts in the field advocate for more stringent regulations governing facilities offering hyperbaric oxygen therapy, especially those providing treatment for unapproved or experimental purposes. Tom Workman, a former director at the Undersea & Hyperbaric Medical Society, stressed the importance of ensuring that only accredited facilities with trained personnel administer hyperbaric therapy to patients.
Meanwhile, Thomas Cooper’s family remains resolute in their pursuit of justice for their son. Harrington revealed their intentions to file a wrongful death lawsuit against the Oxford Centre to shed light on the lapses in safety protocols that contributed to Thomas’s tragic death. The family’s hope is that their legal action will not only secure justice for Thomas but also lead to improved regulation of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to prevent similar incidents from occurring.
As the community mourns the loss of young Thomas Cooper, the conversation surrounding hyperbaric oxygen therapy has shifted towards enhancing safety measures and oversight in wellness centers that offer these treatments. The Cooper family’s quest for justice serves as a poignant reminder of the importance of ensuring the well-being and safety of individuals seeking alternative medical interventions, urging for a reevaluation of the protocols governing hyperbaric oxygen therapy.