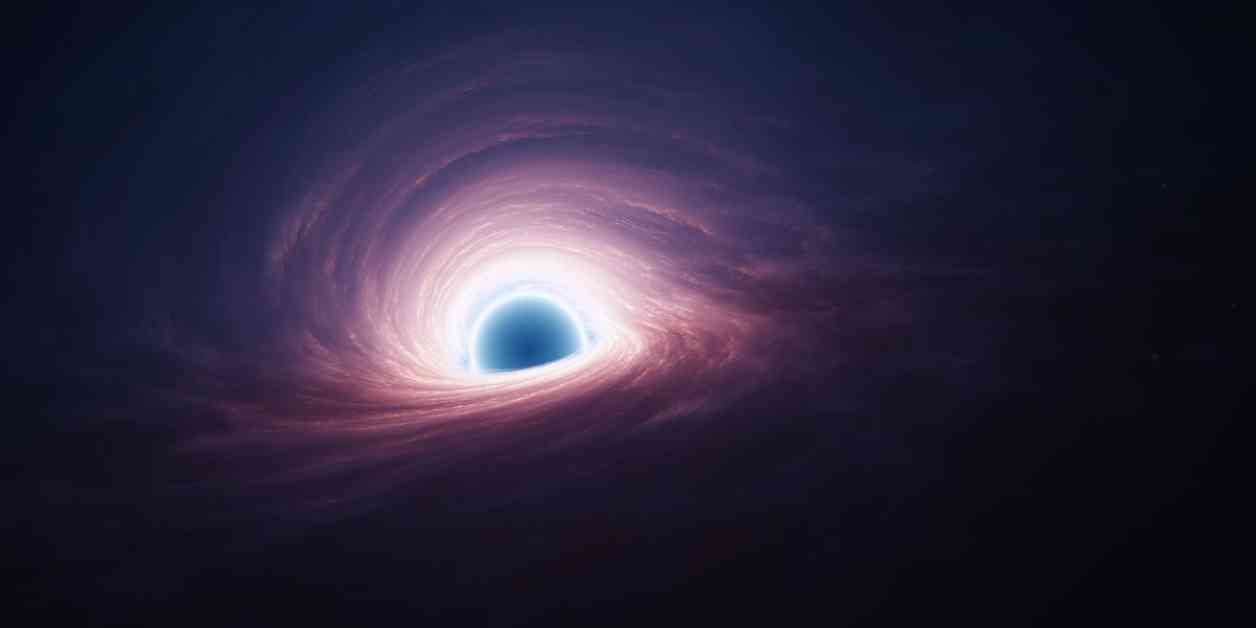
Supermassive Black Hole ‘Starving’ Galaxy: Scientists’ Discovery
A groundbreaking discovery has been made by astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) that sheds light on the mysterious phenomenon of a galaxy being ‘starved’ to death by a supermassive black hole. The galaxy in question, known as GS-10578 or ‘Pablo’s Galaxy’, is located nearly 12 billion light-years away and has long puzzled scientists with its lack of new star formation. However, thanks to the advanced capabilities of the JWST, researchers have finally unraveled the mystery behind this cosmic anomaly.
The Culprit Revealed
The key revelation from the study is the presence of a supermassive black hole within Pablo’s Galaxy that is effectively suffocating the entire galaxy by expelling gas before it has a chance to form new stars. This black hole, with a mass equivalent to 200 billion times that of the sun, is acting as a cosmic gatekeeper, preventing the galaxy from replenishing its star population. Francesco D’Eugeniom, co-lead author of the study and astrophysicist at the University of Cambridge, remarked, “We found the culprit. The black hole is killing this galaxy and keeping it dormant by cutting off the source of ‘food’ the galaxy needs to form new stars.”
Unveiling the Mystery
To unravel the mystery behind Pablo’s Galaxy, researchers directed the JWST towards the galaxy and discovered a dense, cold stream of gas that was obstructing the light from a galaxy situated behind it. This gas mass was found to be greater than the amount required for new stars to form, confirming that the black hole was indeed stifling the galaxy’s ability to generate new stellar bodies. Roberto Maiolino, co-author of the study and professor of experimental astrophysics at Cambridge, emphasized, “We knew that black holes have a massive impact on galaxies and perhaps it’s common that they stop star formation, but until Webb, we weren’t able to directly confirm this.”
The findings of this study have been published in the prestigious Nature Astronomy journal, marking a significant advancement in our understanding of the intricate relationship between supermassive black holes and their host galaxies. This groundbreaking research not only sheds light on the cosmic processes at play within galaxies but also highlights the pivotal role that black holes play in shaping the evolution of the universe.
In conclusion, the discovery of a supermassive black hole ‘starving’ a galaxy to death represents a pivotal moment in the field of astronomy. By utilizing the advanced capabilities of the JWST, researchers have been able to uncover the mechanisms by which black holes can effectively stifle the formation of new stars within galaxies. This discovery not only deepens our understanding of the cosmic forces at play in the universe but also underscores the intricate interplay between black holes and their host galaxies. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos, discoveries such as this serve as a reminder of the awe-inspiring complexity and beauty of the universe we inhabit.