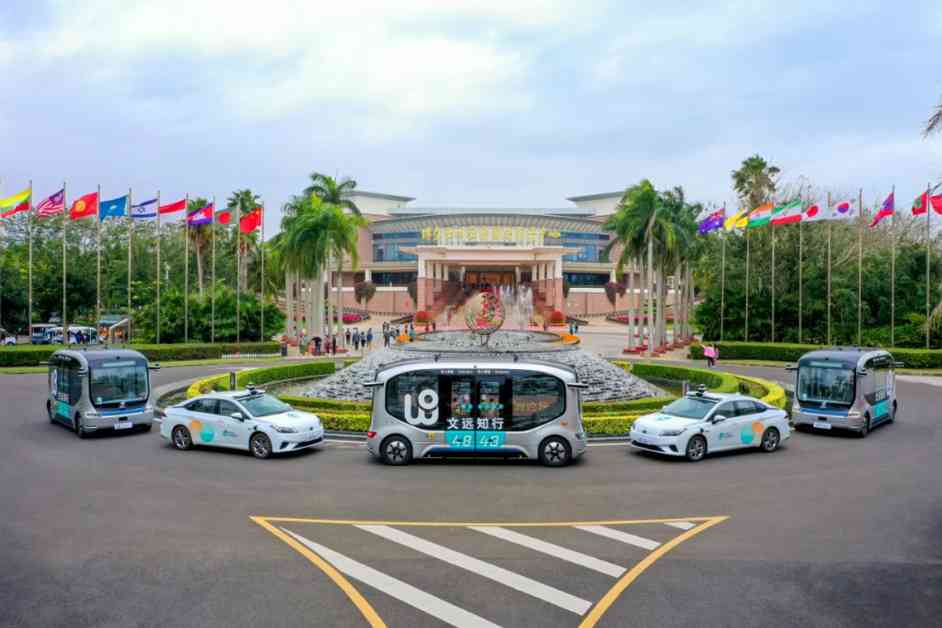
WeRide, a Chinese autonomous vehicle company, has received approval to test its driverless taxis with passengers in California. This milestone comes just before WeRide’s upcoming initial public offering (IPO) on the US stock market, aiming for a valuation of nearly $5 billion. However, amidst this progress, national security concerns regarding Chinese-connected vehicles, including autonomous vehicles, have been raised by the Commerce Department.
WeRide’s Progress in California
As of August 2, WeRide has been granted two permits from the California Public Utilities Commission: a driver pilot permit and a driverless pilot permit. These permits allow WeRide to test its vehicles on public roads with passengers on board. While the former requires a human safety driver, the latter does not. It is essential to note that these permits do not authorize WeRide to charge passengers for rides, and the service remains unavailable to the general public at this time.
While it is unclear if WeRide has begun transporting passengers in its autonomous vehicles, a spokesperson from the CPUC has confirmed that WeRide is permitted to conduct testing in San Jose and surrounding areas, operating a fleet of 12 active vehicles. WeRide has been conducting autonomous vehicle tests without passengers on public roads in San Jose since 2021, following the acquisition of permits from the California Department of Motor Vehicles.
WeRide’s expansion in California has been gradual, with data from the DMV showing that the company’s vehicles accumulated only 42,391 autonomous miles within the state during 2023. In comparison, Waymo, a key player in the autonomous vehicle industry, has surpassed 9 million autonomous miles. WeRide has not disclosed extensive information about its commercialization strategy in California, and their CPUC permit restricts vehicle capacity to fewer than 16 occupants, including the driver.
WeRide’s Global Presence
WeRide positions itself as a leading autonomous driving company globally, operating and conducting testing in 30 cities across seven countries. The company holds permits for autonomous driving on public roads in China, Singapore, the UAE, and the United States. Apart from its robotaxi and robo bus offerings, WeRide is also working on developing Donovan for goods delivery, a robotic street sweeper, and ADAS technology for original equipment manufacturers.
Challenges to Ride-Hailing Workforce
As WeRide and other companies strive to commercialize autonomous vehicles in the US, there is growing concern about the potential impact of robotaxis on China’s extensive ride-hailing industry. The deployment of robotaxis in China is raising fears of job displacement among ride-hailing and taxi drivers.
Liu Yi, a 36-year-old ride-hailing driver in Wuhan, has witnessed the rise of robotaxis in his city. As he watches neighbors order driverless taxis from companies like Apollo Go, a subsidiary of Baidu, he foresees challenges ahead for traditional drivers. With oversupply issues in the construction industry leading to fewer job opportunities, many drivers like Liu Yi are facing uncertainty about their livelihoods in the face of automation.
China’s Approach to Autonomous Vehicles
China has taken a proactive stance towards the deployment of autonomous vehicles, with at least 19 cities in the country conducting trials with robo taxis and robo buses. Notably, seven cities have approved these trials without the need for human-driver monitors, signaling a significant advancement in the autonomous vehicle industry. Companies like Apollo Go, Pony.ai, WeRide, AutoX, and SAIC Motor are leading the way in autonomous vehicle technology in China.
Economists emphasize the importance of finding a balance between creating new jobs and the potential loss of existing jobs due to automation. Tang Yao, an associate professor of applied economics at Peking University, highlights the need for a measured approach to the adoption of autonomous vehicles to ensure a smooth transition for the workforce. While automation may bring about disruptions in the short term, it could benefit China’s economy in the long run, particularly in light of demographic challenges such as an ageing population and a shrinking workforce.
The Future of Autonomous Vehicles
As China races to establish itself as a leader in the global autonomous vehicle market, the potential impact on the ride-hailing workforce remains a critical concern. While the technological advancements in autonomous vehicles hold promise for transportation efficiency, the human cost of rapid automation is a pressing issue that must be addressed.
In conclusion, the deployment of driverless taxis by WeRide in California marks a significant step towards the commercialization of autonomous vehicles. However, the potential challenges faced by the ride-hailing workforce in China underscore the need for a balanced approach to automation that considers both technological advancement and the welfare of workers in the evolving transportation landscape.