Ukraine’s Strategic Advances in Kursk Region
Ukrainian forces have made significant progress in gaining control over Russia’s Kursk region by strategically destroying key bridges over the Seim River. This bold move has not only boosted morale among Ukraine’s population but has also hindered Russia’s ability to respond effectively to the ongoing incursion by Kyiv.
Strategic Destruction of Bridges
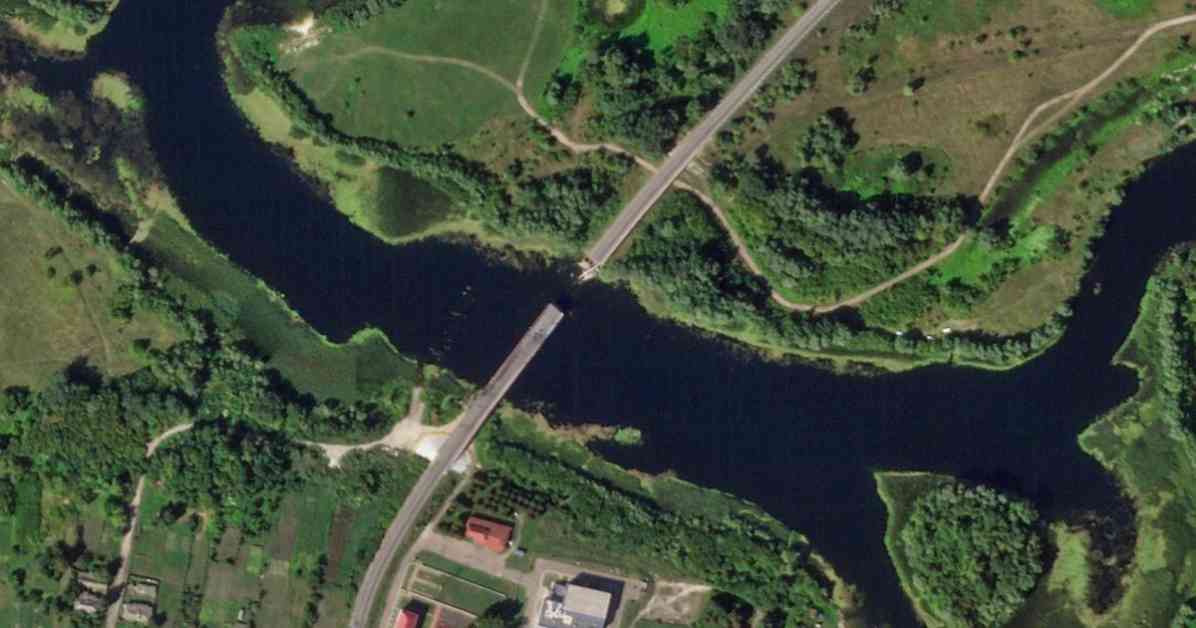
The destruction of all three bridges over the Seim River in the Kursk region has dealt a significant blow to Russian forces operating in the area. By targeting these crucial infrastructure points, Ukraine has effectively limited the movement of Putin’s troops and disrupted their supply routes.
The first bridge in the village of Glushkovo was destroyed on Friday, followed by the second bridge in Zvannoye on Saturday, and finally, the third bridge in Karyzh on Sunday night. These bridges served as vital connections between the Kursk region and the rest of Russia, and their destruction has forced Russian troops to rely on makeshift pontoon bridges for transportation and supplies.
Impact on Russian Response
The attacks on the bridges have already begun to slow down Russia’s response to the Ukrainian incursion, which began on August 6. With their supply routes disrupted and movement restricted, Russian forces are finding it increasingly challenging to counter Ukraine’s advances in the region.
According to a Russian military investigator, Ukraine’s targeted shelling has caused significant damage to the bridges, with one bridge completely destroyed and two others severely damaged. The full extent of the damage is still unclear, but it is evident that Ukraine’s strategic actions are having a tangible impact on the conflict in Kursk.
Strategic Objectives and Achievements
Ukraine’s incursion into the Kursk region is part of a broader strategy to create a buffer zone along the Russian border, preventing future attacks on Ukrainian territory. President Volodymyr Zelensky has emphasized the importance of capturing Russian prisoners of war to use as bargaining chips for the release of captured Ukrainians.
Since the incursion began, Ukrainian forces have made significant territorial gains, capturing 480 square miles and 92 settlements in the Kursk region. This progress has not only demonstrated Ukraine’s military capabilities but has also exposed vulnerabilities in Russia’s defenses and logistics.
In a bold move to disrupt Russia’s military and economic potential, Ukrainian forces targeted an oil depot in the town of Proletarsk, causing a massive fire that burned for three days. This attack was aimed at undermining Russia’s military capabilities and sending a clear message of defiance to Putin’s regime.
Challenges and Consequences
Despite Ukraine’s successes in the Kursk region, challenges remain as Russian forces continue to push towards key strategic locations, such as the city of Pokrovsk in the Donetsk region. The capture of Pokrovsk would compromise Ukraine’s defensive capabilities and supply routes, bringing Russia closer to its goal of capturing the entire Donetsk region.
As the conflict escalates, the humanitarian impact on civilians in the region is becoming increasingly severe. More than 122,000 people have been resettled since the incursion began, with hundreds of firefighters and civilians sustaining injuries in the line of duty.
Conclusion
Ukraine’s strategic advances in the Kursk region have reshaped the dynamics of the conflict with Russia, showcasing the country’s determination and military prowess. By targeting key infrastructure points and disrupting Russian supply routes, Ukraine has gained a significant advantage on the battlefield.
As the conflict continues to unfold, the international community will be closely monitoring the situation in Kursk and its broader implications for regional security and stability. Ukraine’s bold actions have not only raised the stakes in the ongoing conflict but have also highlighted the need for a coordinated and collaborative approach to resolving the crisis.